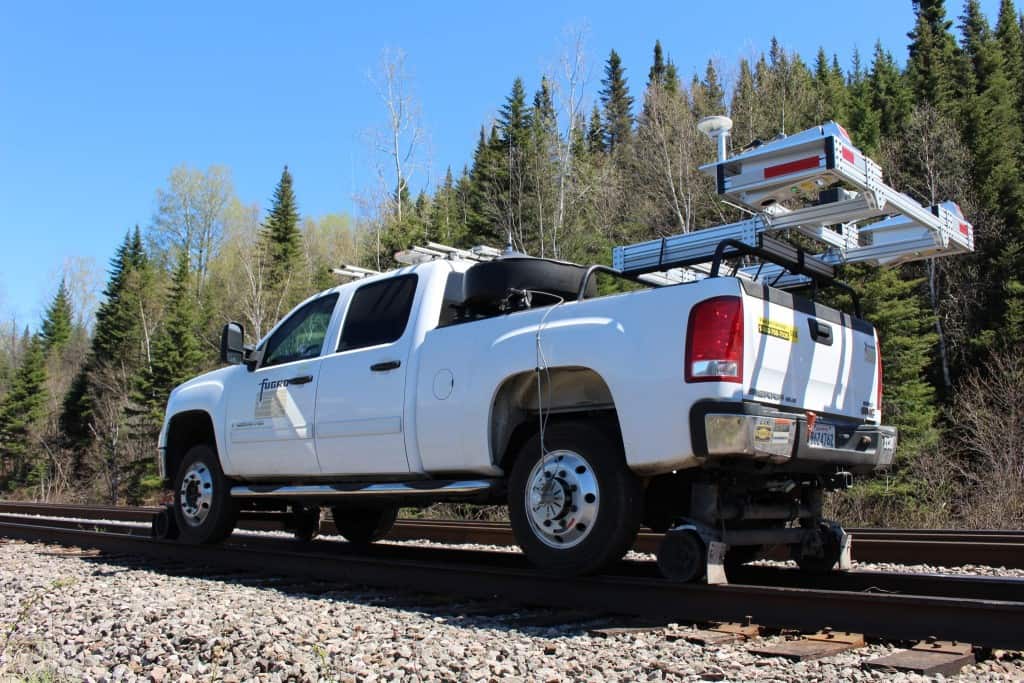
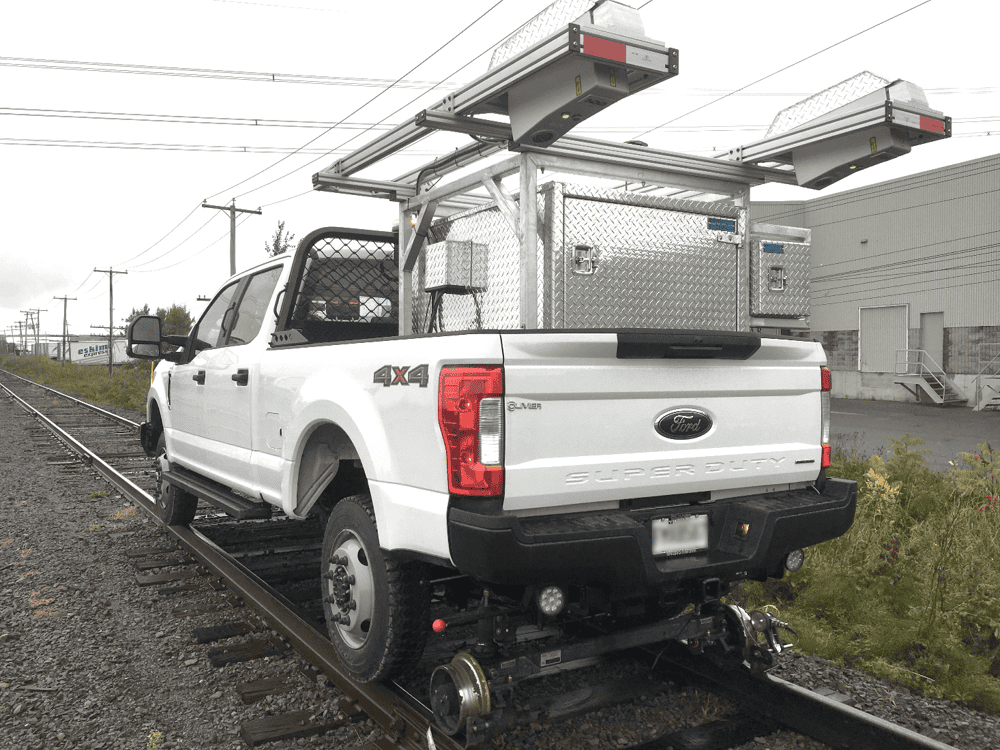



Inspect critical turnout components and assess tie condition automatically — all at up to 120 km/h.
Simultaneous 2D imaging and 3D scanning replace multiple legacy systems in a single pass.
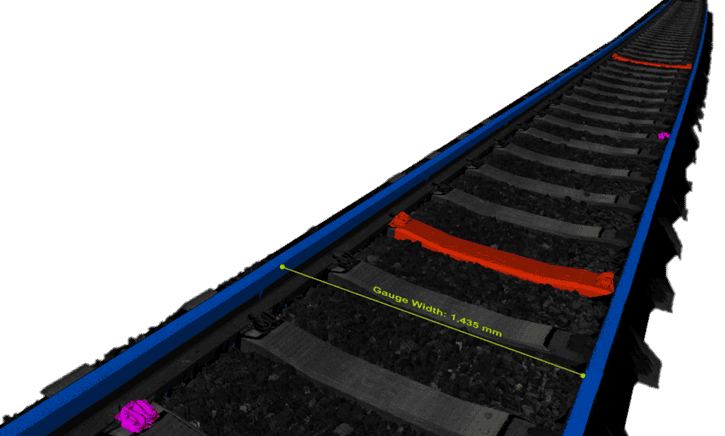
1 mm × 1 mm × 0.1 mm scans deliver unmatched clarity of rails, ties, fasteners, and ballast.
AI-powered analysis ensures consistent, objective results across repeat runs.
Validated in the field and trusted by rail operators globally.
The Pavemetrics® Laser Rail Inspection System (LRAIL™) is a next-generation 3D vision system that transforms railway inspection. In a single pass at speeds up to 120 km/h, LRAIL captures both high-resolution 2D images and 3D profiles of rails, ties, and ballast — delivering unmatched clarity and repeatability.
Powered by advanced Artificial Intelligence, LRAIL automatically detects, measures, and grades all critical components, including ties, clips, joints, switches, crossings, and rail surface wear. The result is a comprehensive, objective inspection that enables railways to prioritize maintenance, extend asset life, and reduce costs — without disrupting operations.
Built on Pavemetrics’ proven LCMS® technology, deployed in over 45 countries worldwide, LRAIL delivers field-validated accuracy that rail operators and regulators trust for safer, more efficient networks.

Operates at up to 120 km/h with full automation and no disruptions.
Compatible with narrow, standard, and wide gauges.
Simultaneous 2D high-resolution imaging and 3D point cloud generation in a single pass.
Automated change detection and grading of ties, fasteners, joints, switches, and crossings.
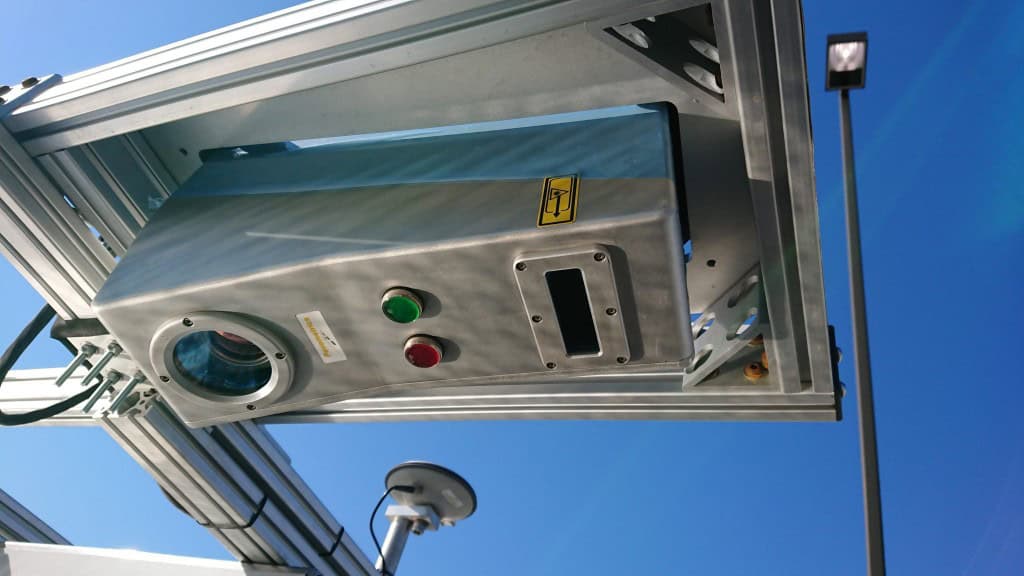
Operates day and night, immune to lighting/shadow conditions, with compact 13 kg sensors in rugged, sealed enclosures.
Anchor inspection, ballast level & fouling, elastic fasteners, rail geometry, rail head profile & wear, road crossings, turnout components, tie condition, tie plates & spikes.
Explore all measurement capabilities and details: View Measurement Capabilities
1 mm transverse, 0.1 mm vertical.
±0.25 mm vertical.
0–120 km/h (track speed operation).
16,666 Hz.
Narrow, standard, and wide gauges.
2D high-resolution images and 3D point clouds, geo-referenced with GPS/IMU.
Compact sensors (13 kg each), low power consumption.
Compatible with high-rail vehicles or dedicated inspection cars.
Day and night, immune to lighting/shadow conditions.
Onboard compression algorithms minimize storage requirements.
LRAIL Comparison to Track Geometry Measuring Trolley (TGMTs) and Manually Operated Devices (MODs)
Owing to the design of TGMTs and MODs, the EN 13848-1:2003+A1:2008 requirements have to be modified. Therefore, this annex lists in tabular form the minimum requirements for each track geometry parameter which can be measured by TGMTs and MODs. Requirements differing from EN 13848-1:2003+A1:2008 are highlighted in bold. The requirements of EN 13848-1:2003+A1:2008 are shown only for comparison purposes.
Authors: Cesar Singh (U.S. Department of Transportation), Yuanchang Xie (University of Massachusetts Lowell)
Summary: In this project led by the US Department of and University of Massachusetts Lowell, the use of commercial remote sensing and spatial information technologies such as Ground Penetrating Radar, laser (LRAIL), GIS and GPS have been applied to passenger rail inspection. The technologies were integrated on a hi-rail vehicle and tested at the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) and Metro St. Louis. While rail transit agencies in the United States rely heavily on visual observation for their weekly track inspections, this manual method is time-consuming, costly and cannot effectively identify subsurface safety hazard. The main objective of this project was to provide a safe, objective and cost-effective solution to rail transit agencies for their weekly track inspections. The conclusions of this project highlight the quality of the collected data and the results generated by the developed algorithms of the LRAIL and suggested that it is a viable and very promising solution to use for track safety inspections.
Authors: Federal Railroad Administration
Abstract: This report documents the successful use of 3D laser scanning, Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNNs), and change detection technology to reliably detect and classify a wide variety of track components and conditions that influence the safety of train operations, and to report changes in these features over time with high precision. This technology advances the state-of-the-art in automated track inspection, going beyond the simple pass/fail assessments typical of current inspection approaches. During the test program, conducted between April 2019 and October 2020, it detected a wide range of both small and large changes related to elastic fasteners, spikes, joint bar gaps, joint bar bolting, crosstie skew, ballast level, and ballast fouling.
Authors: Richard Fox Ivey, Mario Talbot, John Laurent (Pavemetrics)
Abstract: This paper builds on prior work (Deep Learning for Railroad Inspection – Phase 1) to develop a Deep Neural Network that can automatically identify key railway components as a step in the process of automating rail inspection in an effort to overcome the limitations of traditional methods. This new study adds the identification of new railway components (Tie Plates) as well as the automated assessment of their condition.
Authors: Richard Fox Ivey, Mario Talbot, John Laurent (Pavemetrics)
Abstract: Railway networks around the world are an important part of the transportation network and represent billions of dollars of investment. Poorly maintained networks negatively impact asset longevity, schedule performance and pose a serious threat to safety. In order to safeguard against these risks, Railroads typically inspect 100% of their mainline network at least annually and key locations even more frequently. Railroad inspection has traditionally been a manual process with inspectors walking the track or driving slowly in a high-rail vehicle to visually spot problems. This practice is very costly, time consuming, impacts schedule performance (due to the need for track possession), and puts staff at risk. While there have been some recent attempts to modernize the inspection process through the adoption of machine-vision technologies, these technologies are often still reliant on human inspectors manually reviewing images in order to spot defects. Manual review of images suffers from many of the same problems as manual inspections do: it is time consuming, subjective as opposed to being objective, and requires significant amounts of labor. This paper will explore a new approach which makes use of Deep Learning algorithms, specifically a Deep Neural Network, to automatically inspect images and has the potential to overcome these limitations.
Authors: Federal Railroad Administration
Abstract: This report documents the successful demonstration of automated change detection on railroad track. Pavemetrics Systems Inc. performed this research under contract with the Federal Railroad Administration between March and December 2017. The project successfully demonstrated the ability of its Laser Rail Inspection System (LRAIL) to detect changes in fasteners, anchors, spikes, ties, joints, and ballast—as well as record rail stamping information on Amtrak's Harrisburg line.
Authors: Federal Railroad Administration
Abstract: This report details the deployment of Pavemetrics' Laser Rail Inspection System, "LRAIL," for the purposes of automated change detection. The project was conducted between September 2018 and December 2019 at filed locations on Amtrak property and at Pavemetrics' offices in Quebec, Canada. The project involved a combination of field sensor data acquisition, deliberate manual changes in the field, office algorithm development, algorithm testing and validation, and system performance reporting. The extended field trial proved successful. Repeatability, mean, and standard deviation of change measurements were determined and noise floors for each measured parameter were established.







